
GDPR and SAP
The use of personal data by companies, sometimes unjustified and with unclear purposes, has brought the European legislator to regulate the use of these types of data.
In the past, by a specific directive, member states had to adapt individually. Every single state defined its own law about personal data protection. However, the legislative fragmentation generated by every single country on this theme, led every member state to have different managements. In Italy the reference law was Dlgs. 196/2003 “Codice in materia di protezione dei dati personali”.
It’s also because of this that the European parliament decided to start a rationalization of this topic. This was done by the institution of a European regulation, in force from the 25th of May 2018.
The legal institution of the European regulation expects that member states must adapt to this regulation by modifying, if necessary, their national regulations. The European legal institution is called GDPR General Data Protection Regulation 679/2016. In Italy, by the Dlgs. 101/2018 have been modified the previous provisions of Dlgs 196/2003. In Italy, the GDPR, it’s also known as RGPD Regolamento Generale sulla Protezione Dati.
Indice
- What does it change compare with the old legislation?
- Which are the focal points?
- Which are the actions that can be done to increase the accountability in SAP?
- Which are the main SAP tools for the GDPR management?
- How can Aglea help you?

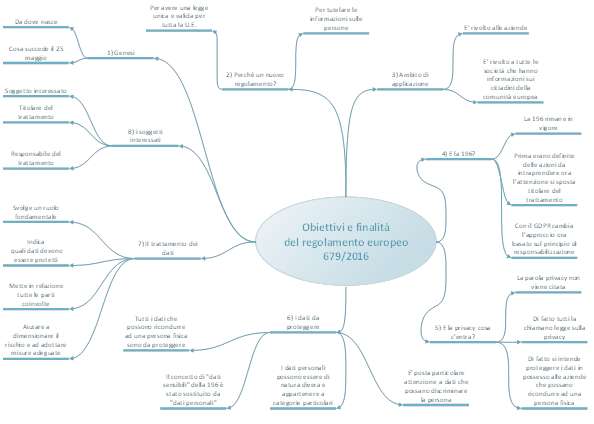
There is an important change to the approach of personal data protection.
In the Dlgs. 196/2003 the protection of data was based on the definition of minimum-security measures. Today, through GDPR, there is risk-based approach.
In other words, companies do not have a list of minimum measures (as it was in the past with the Dlgs 196/2003, annex B), but it has to do a risk based analysis, case by case and has to state which are the measures to adopt in relation to risks
Which are the focal points?
One of the most relevant aspect is the introduction of the treatment register. What is it? Why is it so strategic?
The treatment register represents a company’s list where all treatments of personal data present in the company, are managed. For example:
Payroll office managementSocial media management
Accounting management (in case of references to a physical person)
… so on…
These informations must be defined for each line:
Type of managed dataStakeholders
Processing purposes and methods
Communication and dissemination of data
Retention
For particular categories of data (such as sensible data) a Data Protection Impact Analysis (DPIA) is necessary. This risk-based evaluation will establish which are the gaps that need to be filled in or if what is already present in the company database, is already compliant.
Which are the key figures of this legislation?
ControllerProcessor
DPO - Data Privacy Officer
Data subject
Authority
Which are the actions that can be made to increase the accountability in SAP?
One of the aspects that are cited in the law is the accountability of the controller of data, so all that measures that can improve the general environment of the security of data and of system’s governance.
Some of these measures can be done without the use of additional paid software. Here you find some of the macro areas on which is possible to intervene immediately:
- Authorization and Security concept
- Identity Management
- Log management SIEM (Security Information and Event Management)
- Secure Programming
- Training Security awareness
The definition of an authorization model (SAP Authorization Concept) based on the professional environment (RBAC, Role Based Access Control) can definitely increase the ordinary management of authorization and SAP access, but can also greatly increase system’s governance. Also, the management of segregation of duties (SoD) is an important ally in this environment
The adoption of identity management tools. Today in the average sized environment, it’s not possible the manual management of access. These programs help to concentrate on the governance of the defined model, improving also the ordinary management.
SAP standard logs applications. By default, SAP has lot of logs that can be activated (also if some of those are already activated) that can be exploited. Be careful, logs are always difficult to manage then they are a lot. A SIEM is needed in order to manage logs in a proper way.
Despite it has always been underestimated over the years, the secure programming part, especially in SAP environment, becomes strategic in order to guarantee that all the levels “over it” (application level) is secure.
GDPR training and training security are the element that includes the whole process of compliance (be careful, training must be constant, it’s a process). Check here SAP GDPR Course what we did for privacy officers, an E-Learning course on GDPR (Italian Language).
Which are the main SAP tools for the GDPR management?
Unfortunately, doesn’t exist a unique tool to manage the conformity of the regulation. There are about 20 systems that SAP provides in order to respond to the previsions of the legislation on personal data treatment. Most of them are paid systems
They are:
- SAP Governance Risk and Compliance
- Process Control
- Access Control
- Risk Management
- Audit Management
- Fraud Management
- SAP ILM Information Lifecycle Management
- SAP TDMS Test Data Migration Server
- SAP SSO Single Sign On
- SAP Identity Management (and in cloud version SAP HANA Cloud Platform Identity management services)
- SAP Enterprise Threat Detection
- SAP CVA Code Vulnerability Analysis
- SAP Information Steward
- SAP Process Mining by Celonis
- SAP Read Access Log
- SAP Field Masking (UI Logging e UI Masking)
- SAP Data Privacy Governance
Let’s see how each of these systems can be helpful in the process of GDPR management and in which moment is best to use. The process of conformity of GDPR essentially wants these technical macro-steps:
- Definition and governance of the treatment register
- SAP Data Privacy Governance, gives you the possibility to define in cloud the register of treatments (Record of Processing Activities - ROPA and make the DPIA)
- Search of personal data into systems (clearly after having identified and defined the treatment register)
- SAP Information Steward e Process Mining
- Verify/check access
- SAP GRC Access Control, SAP Identity Management, SAP Single Sign On
- Profiling measures and access control to personal data
- SAP Field Masking (data masking in production systems)
- Management of data retention
- Information Lifecycle Management (ILM)
- Data scrambling in non-productive systems
- SAP TDMS
- Production of a secure software
- SAP Code Vulnerability Analysis
- Definition of control mechanism ICS (Internal Control System). How can I check that what I defined is going to work properly?
SAP GRC Process Control/Risk Management
How can Aglea help you?
We configure and install SAP software for GDPR management. We are SAP Italy lecturers for systems related to GDPR:
- ADM940 - Authorization Concept
- ADM920 - SAP Identity Management
- GRC300 - SAP Access Control Implementation and Configuration
- BIT665 - SAP Information Lifecycle Management (ILM)
We can help you to verify your SAP system’s health by a specific audit on GDPR. It’s not always necessary to buy new software, often you just need to use what you already have.
Check out our certifications (About Aglea) and case histories.
Suggested Post from our SAP Security Blog
Corso GDPR - General Data Protection Regulation
Uno degli aspetti fondamentali del regolamento è quello di effettuare formazione e sensibilizzazione agli addetti al trattamento dei dati personali, così come previsto dall'art. 39 "Compiti del responsabile della protezione dei dati".
Da qui nasce l'idea di Aglea di creare un corso di formazione in modalità e-learning sulle tematiche del GDPR.
Come esportare dati da SAP?

Come controllare i dati che vengono esportati da SAP? Molti utenti devono essere formalmente autorizzati a farlo, fa parte del loro lavoro. È tuttavia fondamentale, soprattutto in ottica GDPR, controllare come e chi esporta eventuali dati in modo non autorizzato dal sistema SAP.
Come farlo? Vediamo alcuni metodi inclusi nella business suite SAP ed altri a pagamento.
SAP DATA Masking, UI Masking, UI Logging
 Dal punto di vista della terminologia SAP è fondamentale sottolineare la differenza tra il termine Masking ed il termine Scrambling. Il primo, masking, far riferimento al mascheramento dei dati in ambienti produttivi. Il secondo, scrambling, fa riferimento alla modifica dei dati in ambienti non produttivi.
Dal punto di vista della terminologia SAP è fondamentale sottolineare la differenza tra il termine Masking ed il termine Scrambling. Il primo, masking, far riferimento al mascheramento dei dati in ambienti produttivi. Il secondo, scrambling, fa riferimento alla modifica dei dati in ambienti non produttivi.


